Radiation is a kind of energy that is mostly invisible to us. UV (ultraviolet) radiation is one kind of radiation that is measured on the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. Sunlight emits UV rays of three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVC radiation is the highest energy UV radiation. UVC rays may cause serious skin and eye burns (photokeratitis). Avoid direct skin UVC exposure and never stare directly into a UVC light source. UVC-induced skin and eye burns heal within a week with no known long-term effects. In this paper you will find UV sanitizer safety in the following topics:
UV Radiation and related risks; Is UV Sanitizer Safe?
Because UVC radiation has a shallow penetration depth, the danger of skin cancer, cataracts, or irreversible eyesight loss is negligible. The form of eye damage caused by UVC produces intense discomfort and sand in the eyes. Eyesight loss might last one to two days. It may happen after seconds to minutes of exposure to UVC light.
What are the dangers of UVC radiation exposure?
UVC radiation has the potential to cause serious skin burns and eye damage (photokeratitis). Direct skin exposure to ultraviolet C radiation should be avoided, and never stare directly into a UVC light source, even for a short while. Skin burns and eye injuries caused by ultraviolet C exposure normally heal within a week, and there is little evidence of long-term harm.
Because UVC radiation has a relatively low penetration depth, the danger of skin cancer, cataracts, and irreversible vision loss is regarded to be quite minimal. Extreme discomfort and a sensation of having sand in one’s eyes are common symptoms of the sort of eye damage related to UVC exposure. Occasionally, individuals are unable to use their eyes for one to two days after an eye injury. It may happen after a short exposure to UVC rays (seconds to minutes), but it is very rare.
What are the hazards of utilizing various UVC lamps?
Some ultraviolet C lights release trace quantities of ultraviolet B radiation. Some UVC lamps give off a lot of radiation, while others give off a lot of radiation for a long time. This could lead to conditions like cataracts or skin cancer, which are caused by cumulative exposure to UVB radiation.
Additionally, certain UVC lamps emit ozone, which may irritate the respiratory passages (nose, throat, and lungs), which is especially dangerous for those who have respiratory sensitivities like asthma and allergies. High levels of ozone gas exposure may potentially exacerbate chronic respiratory disorders such as asthma, as well as increase the likelihood of contracting a respiratory infection. So, you must be careful while using UVC lamps as UV sanitizers.
What is the impact of UV radiation on the body?
Both UVA and UVB radiation have the potential to cause skin damage. Sunburn is a symptom of short-term overexposure to ultraviolet radiation, while premature aging and skin cancer are side consequences of long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Skin and eye sensitivity to ultraviolet light may be increased in people of all skin types who are using certain oral and topical medications. These medications include antibacterials, birth control pills, and benzoyl peroxide treatments, as well as several cosmetics. Check the label and consult with your doctor if you need further information.
Sunlight is not the only source of ultraviolet radiation that you may come into contact with. Among the other sources are:
- Booths for tanning
- Mercury vapor lighting is a kind of fluorescent lighting (often found in stadiums and school gyms)
- Some fluorescent, halogen, and incandescent lights
- Some kinds of lasers
- The known impacts of ultraviolet radiation on health
The skin
UVA stimulates the production of melanin pigment, which is already present in the top skin cells. It produces a tan that emerges swiftly but fades away just as quickly, if not faster. Furthermore, UVA penetrates into the deeper layers of the epidermis, where it damages connective tissue and blood vessels, causing them to rupture. As a consequence, the skin loses its flexibility over time and begins to wrinkle as a result. As a result, high levels of UVA induce accelerated aging of the skin. Furthermore, current research clearly suggests that it may contribute to the development of skin malignancies in certain people. The way this UVA damage happens isn’t entirely clear, but one popular idea is that UVA makes the cell more vulnerable to oxidative stress.
UVB promotes the formation of new melanin, which results in a significant rise in the amount of the dark-colored pigment in a short period of time. This tan has the potential to linger for an extended period of time. UVB also encourages the production of a thicker epidermis by the cells. In other words, UVB is to blame for the darkening and thickness of the outer cell layers, which are the body’s way of protecting itself from more UV damage.
On the other hand, more intense UVB exposure, on the other hand, causes sunburn, which raises your chances of acquiring cancer. The specific process by which UVB causes or promotes cancer is not yet understood. People who suffer from Xeroderma pigmentosum, a rare pigmentation illness, have a reduced capacity to repair DNA damage produced by exposure to ultraviolet light, according to the condition’s description. Given the much higher prevalence of skin cancer among these individuals, it is possible that direct UV damage to DNA is the mechanism through which exposure to UV radiation is linked to the formation of cancer. Some diseases created by UV are: photosensitivity, the appearance of wrinkles, skin cancer. This is no exception to the use of UV sanitizers to be safe.
Getting a suntan in the real world
There is no such thing as a “healthy tan” in the fitness industry! Skin cancer is not prevented by long-term UV exposure, but it may be prevented by wearing protective clothing. While a suntan may seem to be attractive on the surface, it is nothing more than a warning that your skin has been harmed and is attempting to defend itself by becoming darker from sunburn.
The eye
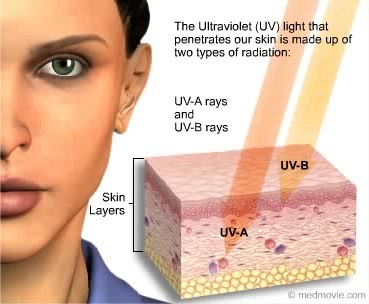
Similarly to the impact on the skin, different solar rays arrive at different times of day and enter the eye at varying depths. However, whereas UVB is completely absorbed by the cornea, UVA is able to permeate through the surface layers and reach the lens. In adults, only 1% or less of incoming UV radiation reaches the retina due to the filtering function of the cornea and lens. In children, this figure is higher.
Although the eye only accounts for less than 2% of the total body surface area, it is the only organ system that allows visible light to penetrate deep into the human body and is thus of critical importance. Several systems have developed throughout the course of human development to protect this very sensitive organ from the detrimental effects of the sun’s rays. Yet, even on a cloudy day, UV radiation exposure may be significant due to the sun. In order to guard against UV damage, the efficiency of these natural defenses must be considered in context. Some diseases created by UV radiation are: photokeratitis and photoconjunctivitis, pterygium, cataracts, and eye cancer. This is no exception to the use of UV sanitizers.

UV interaction with the immune system
The majority of studies to date have focused on UVB, which seems to be more essential than UVA in the development of immunological regulation. However, there has lately been an increase in interest in the effects of UVA on the immune system. A chemical found in the skin is thought to be responsible for the absorption of UV light. The start of recurring cold sore eruptions might be triggered by exposure to sunlight. UVB light seems to impair the immune system’s efficacy; in the case of cold sores, it can no longer regulate the virus Herpes simplex, resulting in infection reactivation.
The impact of sunscreen on the occurrence of cold sores was investigated in research conducted in the United States. After being exposed to UV light even UV sanitizers, 27 of 38 individuals with recurrent Herpes simplex infections developed cold sores. In contrast, none of the patients got cold sores after using a protective sunscreen. As a result, sunscreen may be useful in preventing repeated sun-induced breakouts in addition to minimizing skin-damaging effects.
In recent years, research has shown that exposure to UV levels in the environment may modify the activity and distribution of certain of the cells that drive immunological responses in people. As a result, exposure to the sun may increase the chance of infection or weaken the body’s defenses against skin cancer. High UV levels, particularly in impoverished countries, may reduce the efficiency of immunizations. UV radiation even UV sanitizers has also been linked to the promotion of cancer in two ways: by directly causing DNA damage and by weakening the immune system. Little study has been done so far to explain the possible impact of immunomodulation on cancer development.
Related Articles: Does UV Light Kill Coronavirus?
Do I still need to be cautious since I have dark skin?
You certainly do. Dark-skinned people have a substantially lower chance of acquiring melanoma or non-melanoma skin cancers than fair-skinned ones. They seldom need to use sunscreen and can withstand quite high amounts of UV light without becoming sunburned. However, no matter what your skin color is, there is still a risk of eye injuries and a weak immune system.
The beneficial effects of UV radiation
The sun’s rays bring warmth and light, which improve your overall sense of well-being while also stimulating blood circulation in your body. Some UV light is required by the body due to the fact that it increases the formation of vitamin D. Aside from its significant role in enhancing calcium and phosphorus absorption from meals, vitamin D also plays a critical part in bone growth, immunological function, and the creation of blood cells.
There is no question that a little sunshine is beneficial to your health! During the summer months, however, 5 to 15 minutes of casual sun exposure on the hands, face, and arms two to three times a week is sufficient to keep your vitamin D levels at a healthy level. Even nearer the equator, where UV levels are stronger, even shorter durations of exposure are sufficient to cause skin cancer.
As a result, vitamin D insufficiency is unlikely to occur in the majority of individuals. Those who have extremely minimal sun exposure, such as the housebound elderly or those who have deeply pigmented skin and reside in high-latitude nations where UV levels are generally low, may be exempt from this recommendation. Recognizing the importance of vitamin D, several nations have included vitamin D supplements in everyday foods such as wheat, cereals, and milk. The vitamin D that occurs naturally in our diet is quite uncommon; it is found mostly in fatty fish and cod liver oil, among other sources.
Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, eczema, and jaundice are just a few of the disorders that have been effectively treated using UV or UV sanitizers. Even though this therapeutic use of UV radiation can’t completely get rid of the negative effects of the radiation, the therapy is done under medical supervision to make sure that the benefits outweigh the risks.
Despite these significant responsibilities and medicinal uses, the negative consequences of exposure to ultraviolet radiation exceed the advantages in the vast majority of instances. In addition to the well-known short-term repercussions of excessive sun exposure, such as sunburn or allergic responses, the long-term effects of excessive sun exposure represent a long-term threat to your health. Overexposure to ultraviolet light has been shown to have negative effects on the skin, eyes, and maybe the immune system. Many individuals are unaware of the fact that the effects of UV radiation increase throughout a person’s lifespan. Your current sun exposure habits will affect your future risk of acquiring skin cancer or cataracts. The more time and how often you spend in the sun, the more likely you are to get skin cancer.
A Recommendation for UVC Sterilizers in the Home:
Since the start of the COVID-19 epidemic, there has been an increase in demand for UVC disinfection equipment, as well as its availability. UVC radiation may cause eye and skin problems if used incorrectly or with hazardous sterilisers. UVC damage to the cornea, which causes burning sensations and light sensitivity, as well as burns that cause redness and peeling of the skin, are examples of eye and skin injuries.
The National Environment Agency (NEA) urges people not to use UVC-based disinfection sterilisers or UV sanitizers in their homes. Many home-use sterilisers lack safety safeguards that protect users from unintentional or inadvertent UV radiation exposure. Members of the public are warned not to buy any UV sanitizers (UVC steriliser) goods that lack safety safeguards to avoid accidental exposure and health concerns. According to the NEA, UVC-based disinfection should only be used in an industrial or commercial context with suitable safety features and safe usage practices.
UV sanitizers for disinfection should only be purchased by members of the public if the UVC sources are appropriately confined with safety engineering elements that prevent people from being exposed to UVC radiation. The following are some examples of safety engineering features:
a) When a person or animal approaches a portable UVC lamp or desk light, safety measures such as motion sensors would immediately turn off the UVC source. They protect the user and other people in the area from getting sunburned by mistake.
b) In the case of handheld UV sanitizers/portable UVC wands, safety features such as gravity sensors would immediately turn off the UVC source when the device is pointed upward. Because of these safety safeguards, UVC radiation is not emitted into the user’s eyes. UVC light should not be aimed towards the user’s skin or eyes while utilizing such gadgets.
c) When a person or animal approaches a UVC bulb or tube light, safety measures such as motion sensors would immediately turn off the UVC source.
d) Safety features for UVC disinfection boxes should include the ability to turn off the UVC light while the disinfection box is open.
Related Articles: What Is Ultraviolet Light?

According to the NEA, users should prevent direct skin exposure to UVC radiation and avoid staring directly at a UVC light source. If a UV sanitizer is bought that doesn’t have any of the above safety engineering features, NEA encourages customers to stop using it right away, especially if the device is meant for skin use.
The NEA has been working with large merchants to aggressively remove UV sanitizers from store shelves that are dangerous and represent a risk of UVC radiation exposure. It has been urged that all physical establishments and online sales platforms do not offer UV sanitizers items that are harmful to customers.
Approximately 8,000 ads for dangerous UV sanitizers have been taken down from internet marketplaces thus far. While the NEA has made every effort to collaborate with major online sales platform operators in this respect, the public is encouraged to exercise caution and attention while buying UV sanitizers due to the large number of shops that may advertise on online sales platforms from time to time.
Operators of online sales platforms including Amazon, Carousell, Ezbuy.sg, Qoo10.sg, and Shopee have been proactive in removing hazardous UVC sterilizers from their sites. Other online sales platforms should follow the lead set by the NEA and quickly remove dangerous UV sanitizers items from their stores.

