From the very beginning of human history, there have been lots of inconveniences on the way of evolution. From the basic issues to mandatory requirements to survive like finding shelter, clean water, and food; Meanwhile, facing natural disasters! Using our brain, we have been able to fulfill our needs and speed up our progression sequence. Our foremost enemy has been Viruses and Bacteria infections and probably remains to be this way in the future. Often, sociologists believe that the closest form of life in comparison with human beings is a Virus; They both build-up a colony and ruin whatever is around them for the sake of survival! Our recent enemy has been this infectious virus known as COVID-19. The same human intelligence which helped us to improve ourselves during our evolution is still struggling with a solution for the very basic/routine viruses like Herpies or even more complex ones like HIV. Corona Virus has just been like its other family members remaining with no absolute answer to be solved; Yet, can be harnessed somehow! To do that is easy; JUST STICK WITH THE HYGIENIC PROTOCOLS AND SOCIAL DISTANCING. What you are about to read is “Inspired by the sun, Sanitizes by nature”; Accordingly, The general information of Ultra Violet, types and it`s effects on Corona Virus will be discussed.
DEFINITION OF ULTRAVIOLET
Firstly, you need to know what UV is?! What is the bright side? And it`s usage…. Although Ultra Violet produced by Sun or human-made sources is a member of the invisible light family and is the fountain of Vitamine D; Hence, it has its cons for the human body. It is used for various purposes like purifying water, food, Medical Equipments, Industrial Goods, Physiotherapy, etc.
TYPES OF ULTRAVIOLET
Secondly, you need to get to know different of UV; In which divides into 3 categories A, B, and C (also known as UVA, UVB, and UVC ). The whole UVC and most of UVB are being absorbed by the Ozone layer, so this is only UVA that reaches the earth`s surface. One of the pros of UV exposure is being the source of Vitamin D which is necessary for human health. Also helps to gain Calcium and Phosphorus from meals, resulting in bone growth. WHO-World Health Organization- recommends 5-15 minutes of sunlight, 2-3 times per week.
ATTRIBUTES OF ULTRAVIOLET RAYS
Ultra Violet has the maximum efficiency in Bactria infections elimination without any chemical pollution; In fact, it sanitizes surfaces with no human interaction and no chemical material at all. UV light radiates so desired surface(s) with no need for a tank/storage for sanitizing material.
Disadvantages of UV on Coronavirus?!
According to the fact that UVC can kill 99.9% of viruses-including the COVID family-, so it also removes the other microorganisms resistant to other chemical materials. Chemics are tremendously hazardous to our lungs, thanks to Ultra Violet we don`t need more of those to be produced; so it doesn`t lead to any extra gas release/ chemical tastes! If UVC radiates on chemical materials, it won’t change their quality; Hence, maintaining their physical identity, too. There have been no reports of skin allergic reactions until the present moment. Replacing UV with traditional chemical solutions is not only good for plants and earth, but a top-notch achievement to save our environment.
UV EFFECTS ON CORONA VIRUS
The very first and most important effect of using UV on the environment is in water usage and producing less garbage. Since UV is not a chemical item, it leaves no poisonous ruin. But maybe some specific chemical materials could be affected by its rays. The common belief is that they mostly turn into more harmless forms; yet, more researches are required to admit that! What we are sure of is the bold part of sanitizing via UV are the lamps. These lamps must be able to produce rays in-between 200-300nm with acceptable performance/lifetime. lamps transform the electricity to ultraviolet light energy.
To recap; Nowadays, sanitizing by UV is considered the fastest and most efficient way to kill germs, bacteria/virus removal even in big outdoor areas with the tiniest damage to the earth. Being in touch with chemics like washing hands or aspiration of strong sanitizers is damaging our skin and inhalation system dramatically. Using UVC includes none of the issues above; And you will fulfill the goal to kill 99.9% of viruses.
FAQ – Mostly asked questions
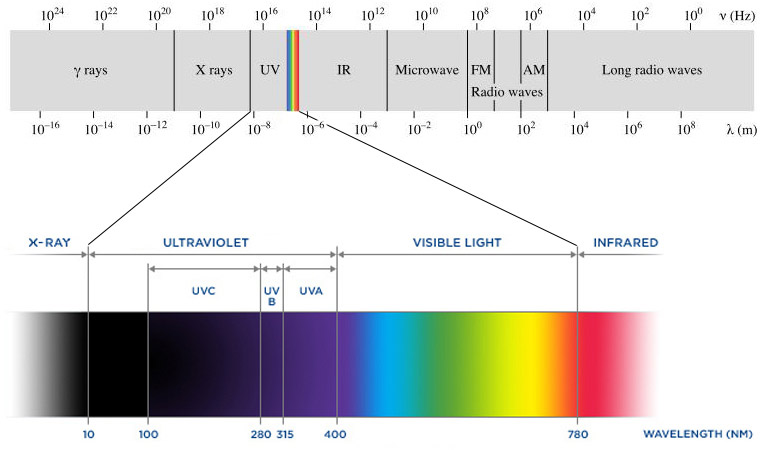
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength from 10 (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. It can also damage skin and/or give a painful sunburn.
Ultraviolet means u0022beyond violetu0022 (from Latin ultra, u0022beyondu0022), violet being the color of the highest frequencies of visible light. Ultraviolet has a higher frequency (thus a shorter wavelength) than violet light. UV radiation was discovered in 1801 when the German physicist Johann Wilhelm Ritter observed that invisible rays just beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum darkened silver chloride-soaked paper more quickly than violet light itself. He called them u0022(de-)oxidizing raysu0022 (German: de-oxidierende Strahlen) to emphasize chemical reactivity and to distinguish them from u0022heat raysu0022, discovered the previous year at the other end of the visible spectrum. The simpler term u0022chemical raysu0022 was adopted soon afterward, and remained popular throughout the 19th century, although some said that this radiation was entirely different from light (notably John William Draper, who named them u0022tithonic raysu0022). The terms u0022chemical raysu0022 and u0022heat raysu0022 were eventually dropped in favor of ultraviolet and infrared radiation, respectively. In 1878, the sterilizing effect of short-wavelength light by killing bacteria was discovered. By 1903, the most effective wavelengths were known to be around 250 nm. In 1960, the effect of ultraviolet radiation on DNA was established. The discovery of ultraviolet radiation with wavelengths below 200 nm, named u0022vacuum ultravioletu0022 because it is strongly absorbed by the oxygen in the air, was made in 1893 by the German physicist Victor Schumann.
UV light (specifically, UVB) causes the body to produce vitamin D, which is essential for life. Humans need some UV radiation to maintain adequate vitamin D levels. According to the World Health Organization. There is no doubt that a little sunlight is good for you! But 5 to 15 minutes of casual sun exposure of hands, face, and arms two to three times a week during the summer months is sufficient to keep your vitamin D levels high. Vitamin D can also be obtained from food and supplementation. Excess sun exposure produces harmful effects, however. Vitamin D promotes the creation of serotonin. The production of serotonin is in direct proportion to the degree of bright sunlight the body receives. Serotonin is thought to provide sensations of happiness, well-being, and serenity to human beings.

